What is GraalVM?
GraalVM is a high-performance, embeddable, polyglot virtual machine for running applications written in JavaScript, Python, Ruby, R, JVM-based languages like Java, Scala, Kotlin, and LLVM-based languages such as C and C++.
Here is the Official doc link
Hmm… Okay, I have to see it.
Let’s install
Below is the way I installed GraalVM Community Edition on Ubuntu 18.04. For other platform, the official doc installation guide is here.
# update this number to latest version from here: https://github.com/oracle/graal/releases
version=1.0.0-rc15
wget https://github.com/oracle/graal/releases/download/vm-${version}/graalvm-ce-${version}-linux-amd64.tar.gz
tar -xvzf graalvm-ce-${version}-linux-amd64.tar.gz
# clean up
rm graalvm-ce-${version}-linux-amd64.tar.gz
# to wherever you want.
mv graalvm-ce-1.0.0-rc15/ ~/bin/graalvm
# if you want to make it permanent, put this in your bashrc
export PATH=$HOME/graalvm/bin:$PATH
Now that your graalvm/bin in your path, you’ll get the GraalVM versions of those runtimes.
before:
$ js --version
v8.10.0
now:
$ js --version
Graal JavaScript 1.0 (GraalVM CE Native 1.0.0-rc15)
Now let’s play with the Polyglot Shell
The Polyglot Shell is useful to quickly test interactive Graal languages. This is how you can start it:
$ polyglot --jvm --shell
GraalVM MultiLanguage Shell 1.0.0-rc15
Copyright (c) 2013-2019, Oracle and/or its affiliates
JavaScript version 1.0
Usage:
Use Ctrl+L to switch language and Ctrl+D to exit.
Enter -usage to get a list of available commands.
js>
Ah, it is listing only JavaScript. Got to install “python component” to run Python
gu install python
Now invoke it again
$ polyglot --jvm --shell
GraalVM MultiLanguage Shell 1.0.0-rc15
Copyright (c) 2013-2019, Oracle and/or its affiliates
JavaScript version 1.0
Python version 3.7.0
Usage:
Use Ctrl+L to switch language and Ctrl+D to exit.
Enter -usage to get a list of available commands.
js> console.log('hello')
hello
python> print('hello')
hello
python>
Oh yay!
For just python interactive shell
$ graalpython
Python 3.7.0 (Thu Apr 04 19:04:32 UTC 2019)
[GraalVM CE, Java 1.8.0_202] on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
Please note: This Python implementation is in the very early stages, and can run little more than basic benchmarks at this point.
>>> print('hello')
hello
>>>
Debugger?
Debugger is available to all the GraalVM languages.
Let’s play with it. Prep the FizzBuzz program in python fizzbuzz.py
def fizzbuzz(n):
if n % 3 == 0 and n % 5 ==0:
return 'FizzBuzz'
if n % 3 == 0:
return 'Fizz'
if n % 5 == 0:
return 'Buzz'
return n
if __name__ == '__main__':
for n in range(1, 21):
print(fizzbuzz(n))
Let’s start debugger
$ graalpython --jvm --inspect fizzbuzz.py
Debugger listening on port 9229.
To start debugging, open the following URL in Chrome:
chrome-devtools://devtools/bundled/js_app.html?ws=127.0.0.1:9229/2c9f9fb0-8067ef52f64c8
- Open the URL in Chrome
- Click “Add folder to workspace” on the left to navigate the folder your fizzbuzz.py is located
- Open fizzbuzz.py from Workspace and place breakpoint then resume script execution
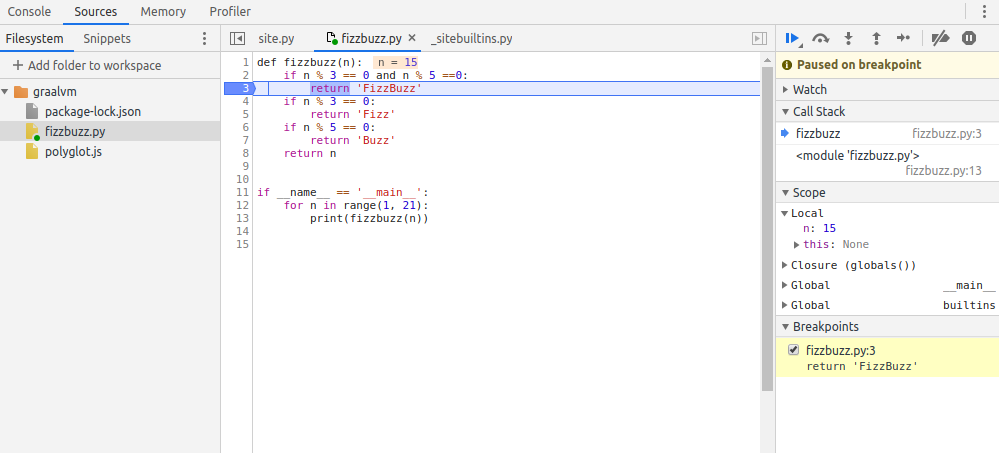
Wow, that’s kind of impressive!
Web app in multiple languages
So this example is from this article
Let’s create polyglot.js
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
const BigInteger = Java.type('java.math.BigInteger')
app.get('/', function (req, res) {
var text = 'Hello World from Graal.js!<br> '
// Using Java standard library classes
text += BigInteger.valueOf(10).pow(100)
.add(BigInteger.valueOf(43)).toString() + '<br>'
// Using R interoperability to create graphs
text += Polyglot.eval('R',
`svg();
require(lattice);
x <- 1:100
y <- sin(x/10)
z <- cos(x^1.3/(runif(1)*5+10))
print(cloud(x~y*z, main="cloud plot"))
grDevices:::svg.off()
`);
res.send(text)
})
app.listen(3000, function () {
console.log('Example app listening on port 3000!')
})
Let’s install dependencies:
First r component
gu install r
Next npm package express
npm install express
Let’s start the app
node --polyglot --jvm polyglot.js
Ta-da!
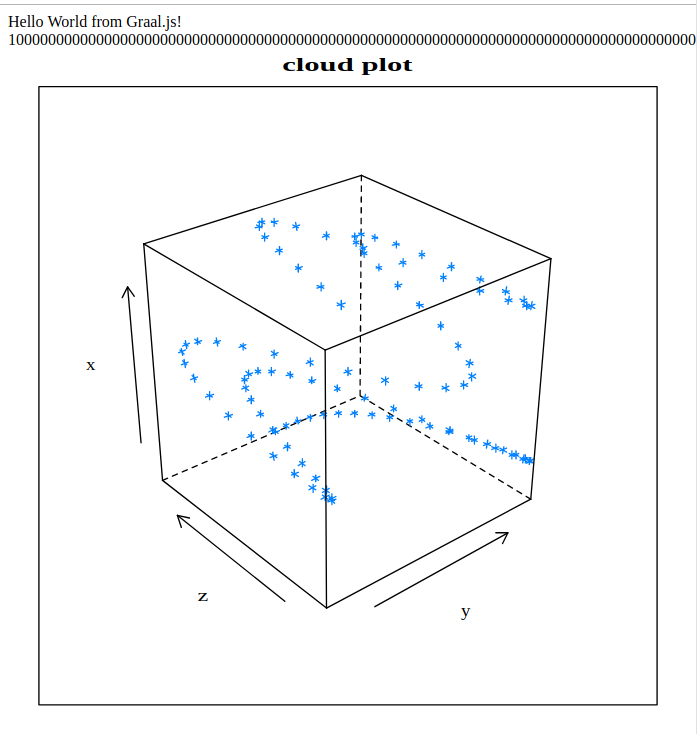
Cheers!